Are you curious to know what is the greater omentum? You have come to the right place as I am going to tell you everything about the greater omentum in a very simple explanation. Without further discussion let’s begin to know what is the greater omentum?
What Is The Greater Omentum?
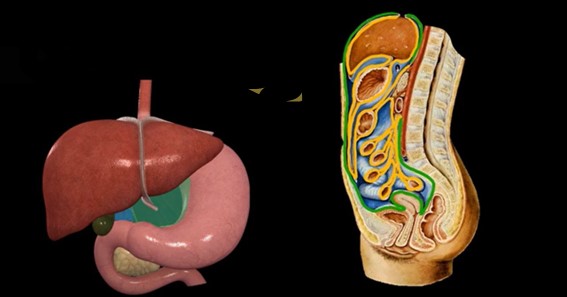
The greater omentum is a sheet of fatty tissue that is attached to the greater curvature of the stomach and covers the intestines. It is a highly vascularized structure that plays an important role in the immune system and serves as a protective barrier for the abdominal organs. In this blog, we will discuss in detail what the greater omentum is, its anatomy and function, and its clinical significance.
Anatomy Of The Greater Omentum
The greater omentum is a large, double-layered fold of peritoneum that hangs down from the greater curvature of the stomach and covers the intestines. It is a highly vascularized structure that contains a network of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and immune cells. The greater omentum is attached to the stomach by the gastrocolic ligament and to the transverse colon by the transverse mesocolon.
The greater omentum is divided into two layers: the superficial layer, which is composed of adipose tissue, and the deep layer, which contains lymphoid tissue and blood vessels. The two layers are separated by connective tissue that contains nerve fibers and lymphatic vessels.
Click here – What Is Vikrell?
The Function Of The Greater Omentum
The greater omentum has several important functions in the body. Firstly, it serves as a protective barrier for the abdominal organs. It can wrap around and isolate areas of inflammation or infection, helping to prevent the spread of disease.
The greater omentum also plays an important role in the immune system. It contains a large number of immune cells, including macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells, which help to fight infections and maintain homeostasis in the body.
Additionally, the greater omentum is involved in metabolic processes. It contains adipose tissue that can store and release energy as needed, and it can also produce hormones and cytokines that affect metabolism.
Clinical Significance Of The Greater Omentum
The greater omentum can be involved in several disease processes. For example, it can become inflamed in response to infection or injury, resulting in a condition known as omental torsion. Omental torsion is a rare condition that can cause severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and fever, and can be treated with surgery to remove the affected tissue.
In addition, the greater omentum can be a site for the spread of cancer. Tumors that originate in the abdominal organs can spread to the greater omentum, and tumors that originate in the greater omentum can spread to other parts of the body. Omental metastases are commonly seen in the advanced stages of ovarian cancer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the greater omentum is a sheet of fatty tissue that is attached to the greater curvature of the stomach and covers the intestines. It has several important functions, including serving as a protective barrier, playing a role in the immune system, and being involved in metabolic processes. While it can be involved in several disease processes, including omental torsion and omental metastases, the greater omentum plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and protecting the abdominal organs.
For more information like this visit Weji
FAQ
What Is The Function Of Greater Omentum?
The function of the greater omentum
The greater omentum prevents the parietal and visceral peritoneum of the abdominal cavity from adhering to each other. For example, it prevents the parietal peritoneum lining the anterior abdominal wall from sticking to the visceral peritoneum of the ileum.
What Is The Omentum And What Does It Do?
The Omentum is a large flat adipose tissue layer nestling on the surface of the intra-peritoneal organs. Besides fat storage, omentum has key biological functions in immune regulation and tissue regeneration.
Is Omentum The Same As Belly Fat?
what’s an Omentum? Omentum Fat by any other name is still the same…Belly Fat, Beer Gut, Abdominal Fat, Spare Tire, Visceral Fat, Intra-Abdominal Adiposity (IAA)…it’s the “sheet” of unhealthy fat located deep inside the abdomen, underneath the muscles in your stomach.
Can Omentum Grow Back After Removal?
No. This misunderstanding comes from the fact that your omentum is part of your peritoneum, the tissue that lines your abdominal cavity and wraps around your organs. Peritoneal tissue is known to have rapid healing properties. But no, your omentum won’t grow back after being removed.
What Organs Are Under The Greater Omentum?
The greater omentum is a 4-layered fold of peritoneum that extends down from the stomach, covering much of the colon and small bowel. The layers are generally fused together caudal to the transverse colon. The gastrocolic ligament is part of the greater omentum.
I Have Covered All The Following Queries And Topics In The Above Article
What Is The Greater Omentum Composed Of
The Greater Omentum Is What To The Small Intestine
What Is The Greater Omentum Comprised Of
What Organ System Is The Greater Omentum In
What Is The Function Of The Greater Omentum
What Is The Greater Omentum Composed Of
What System Is The Greater Omentum Part Of
Greater Omentum Function
Lesser Omentum
Greater Omentum Contents
Lesser Omentum Function
Greater Omentum Layers
What Are The 4 Layers Of The Greater Omentum
Omentum Cancer
What Is The Greater Omentum
What is greater omentum?